Embark on a journey to discover the significance of ideal body weight for amputees. This guide unveils the intricate relationship between amputation, body composition, and overall health, providing invaluable insights and practical strategies for weight management.
As we delve into the topic, we’ll explore how amputation impacts metabolism, body fat distribution, and lean muscle mass. We’ll also examine the influence of activity level, functional capacity, and prosthetic considerations on weight management.
Body Composition Considerations

Determining the ideal body weight for amputees involves careful consideration of body composition. Body fat percentage plays a crucial role in assessing healthy weight ranges, as it indicates the proportion of fat mass relative to lean muscle mass.
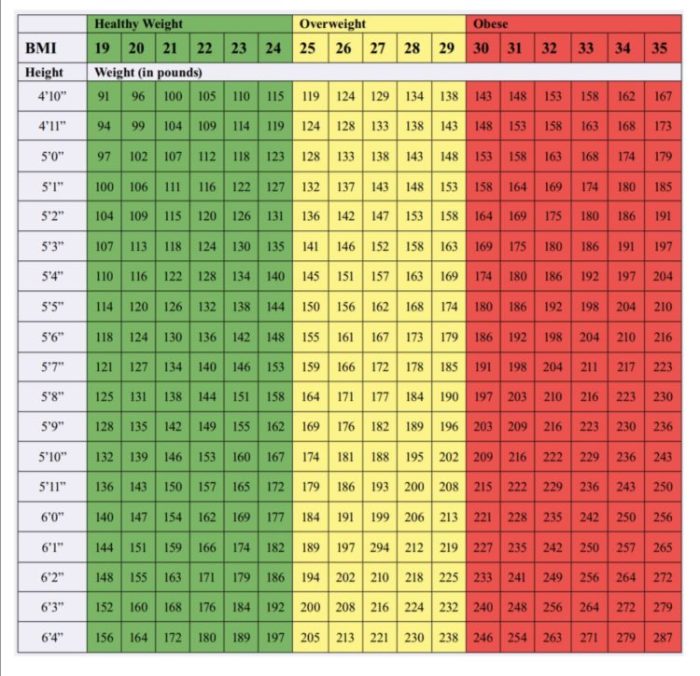
Maintaining a healthy body weight is essential for amputees, as it can impact mobility and overall well-being. Just like the vast and diverse landscapes of natural Texas , the ideal body weight for amputees varies depending on individual factors. It’s crucial to consult with healthcare professionals to determine the optimal weight range that supports mobility, comfort, and overall health.
Amputation significantly impacts body composition and metabolism. The loss of a limb alters energy expenditure, leading to changes in body fat distribution and lean muscle mass. Understanding these changes is essential for developing personalized weight management strategies for amputees.
Impact on Lean Muscle Mass
Research has shown that amputation can lead to a decrease in lean muscle mass, particularly in the affected limb and surrounding areas. This loss of muscle tissue can contribute to reduced strength, mobility, and overall functional capacity. Preserving and rebuilding lean muscle mass is therefore a key consideration in weight management for amputees.
Activity Level and Functional Capacity

An amputee’s activity level significantly influences their ideal body weight. Higher activity levels demand more energy expenditure, necessitating a higher calorie intake to maintain a healthy weight.
Metabolic equivalents (METs) measure the energy cost of physical activities. One MET is equivalent to the energy expenditure of sitting at rest. Activities with higher MET values require more energy, leading to increased calorie burn. For instance, walking at a moderate pace corresponds to approximately 3 METs, while running at a vigorous pace corresponds to around 8 METs.
Assessing Functional Capacity
Assessing functional capacity involves evaluating an amputee’s ability to perform daily tasks and activities. Factors such as mobility, balance, and endurance are considered. A comprehensive assessment can help determine appropriate activity levels and energy requirements, thereby informing body weight goals.
For example, an amputee with a lower limb amputation may have reduced mobility and endurance, resulting in a lower MET expenditure compared to an amputee with an upper limb amputation. This difference would be reflected in their respective calorie needs and ideal body weight.
Prosthetic Considerations
Prosthetics play a significant role in determining the ideal body weight for amputees. The weight, design, fit, and alignment of a prosthesis directly impact weight distribution and energy expenditure, influencing overall body composition.
Prosthetic Weight and Design:The weight of a prosthesis can vary depending on the materials used, the type of amputation, and the level of functionality required. Heavier prosthetics can add additional weight to the body, affecting balance and gait. Design factors such as the shape, size, and articulation of the prosthesis can also influence weight distribution.
Prosthetic Fit and Alignment
Proper prosthetic fit and alignment are crucial for weight management. An ill-fitting or misaligned prosthesis can cause discomfort, pain, and abnormal gait patterns, leading to increased energy expenditure and weight gain. A well-fitted prosthesis distributes weight evenly, promotes efficient movement, and reduces the risk of secondary complications.
Prosthetic Technology Advancements
Advancements in prosthetic technology have significantly impacted weight management for amputees. Lighter materials, improved designs, and advanced manufacturing techniques have resulted in the development of prosthetics that are more lightweight and durable. These advancements allow amputees to engage in a wider range of activities, burn more calories, and maintain a healthier weight.
Nutritional Needs

Maintaining an ideal body weight as an amputee requires careful attention to nutritional intake. Calorie needs vary based on factors like activity level and prosthetic use, but general recommendations can provide a starting point.
Macronutrient distribution is also crucial. Protein is essential for muscle maintenance and recovery, especially after amputation. Carbohydrates provide energy, while fats support hormone production and cell function.
Calorie Intake, Ideal body weight for amputees
Calorie requirements for amputees vary widely. Factors like prosthetic use, activity level, and individual metabolism influence needs. A registered dietitian can provide personalized recommendations based on these factors.
Macronutrient Distribution
A balanced macronutrient distribution is key for amputees. Protein intake should be higher than for non-amputees, typically around 1.2-1.7 grams per kilogram of body weight per day. This supports muscle maintenance and recovery.
Carbohydrates provide energy and should make up 45-65% of total calories. Whole grains, fruits, and vegetables are good sources.
Fats are essential for hormone production and cell function. Healthy fats, such as those found in avocados, nuts, and olive oil, should make up 20-35% of total calories.
Hydration
Hydration is crucial for overall health and weight management. Amputees may have increased fluid needs due to sweating and increased respiration. Aim for 8-10 glasses of water per day.
Weight Management Strategies

Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for amputees to improve mobility, reduce pain, and enhance overall well-being. Effective weight management strategies include exercise, dietary modifications, and lifestyle changes.
Setting realistic weight loss goals is essential. Aim for a gradual loss of 1-2.5 pounds per week, as rapid weight loss can be unsustainable and detrimental to health. Monitor your progress regularly by tracking weight, body measurements, and clothing fit.
Make adjustments to your plan as needed based on progress and feedback from healthcare professionals.
Exercise
Regular physical activity is vital for weight management in amputees. Choose activities that are enjoyable and tailored to your abilities. Focus on exercises that improve cardiovascular health, build muscle mass, and increase calorie expenditure. Consult with a physical therapist or certified personal trainer for personalized exercise recommendations.
Diet
A balanced and nutritious diet is essential for maintaining a healthy weight. Prioritize whole, unprocessed foods such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats. Consider consulting with a registered dietitian for personalized nutrition guidance.
Lifestyle Modifications
In addition to exercise and diet, lifestyle modifications can contribute to weight management. Prioritize adequate sleep, as sleep deprivation can disrupt hormones that regulate appetite and metabolism. Manage stress effectively through techniques such as yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature.
Health Implications of Weight Management: Ideal Body Weight For Amputees
Maintaining an ideal body weight is crucial for amputees as it significantly impacts their overall health and well-being. Let’s explore the potential benefits and risks associated with weight management.
Benefits of Ideal Body Weight
- Improved Mobility and Function:Excess weight can strain the prosthetic components and hinder amputees’ ability to move comfortably and efficiently.
- Reduced Risk of Skin Problems:Overweight individuals are more prone to skin irritation and sores due to increased pressure on the residual limb.
- Enhanced Cardiovascular Health:Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular complications.
- Improved Metabolic Health:Obesity can lead to insulin resistance and diabetes, which can negatively impact amputees’ overall health.
- Increased Confidence and Self-Esteem:Achieving an ideal body weight can boost self-confidence and improve amputees’ overall quality of life.
Risks of Overweight or Underweight
- Increased Strain on Prosthetic Components:Excess weight can put excessive stress on prosthetic devices, leading to premature wear and tear.
- Skin Complications:Overweight amputees are more susceptible to skin breakdown, ulcers, and infections.
- Increased Risk of Falls:Obesity can impair balance and coordination, increasing the risk of falls and injuries.
- Cardiovascular Problems:Overweight and underweight amputees are at an increased risk of heart disease and other cardiovascular complications.
- Metabolic Issues:Both obesity and underweight can lead to metabolic disorders, such as diabetes and malnutrition.
Research indicates that maintaining an ideal body weight can significantly improve health outcomes for amputees. Studies have shown that amputees who are overweight or underweight have a higher risk of developing chronic diseases, skin problems, and functional limitations compared to those who maintain a healthy weight.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the recommended calorie intake for amputees?
Calorie intake varies depending on individual needs, but amputees generally require higher calories than non-amputees due to increased energy expenditure.
How does amputation affect body composition?
Amputation can lead to changes in body composition, including decreased muscle mass and increased body fat percentage.
What is the role of prosthetic weight in weight management?
Prosthetic weight can impact overall body weight and distribution, and proper fit and alignment are essential for optimal weight management.